Explore the collection
Showing 13 items in the collection
13 items
图书
Our Stories: Women in COVID-19 in China
This is the fourth issue of the “Our Stories” series published by WeChat public account “We and Equality,”, a compilation of 20 oral narratives from Chinese people who lived through the COVID-19 pandemic firsthand, and a personal reflection by the author of this issue, Qiao Yilin. The editors hope to “document the history of ordinary people, to combat the forgetting that should never have happened, and to present the real experiences, feelings, and voices of all of us–to help us remember what has happened to us.”
The interviewees in this volume are diverse, including those of different ages, educational background, ethnicities, physical and mental status, sexual orientations,marital status, and mobility. They shared their own memories of the pandemic, including facing threats to their survival due to food shortage, not being able to take anti-depression medication due to the lockdown, international students having a hard time returning to China, people with hearing impairments facing various inconveniences, and the discrimination faced by those who had recovered from COVID-19Although primarily focusing on experiences and feelings during the pandemic, many interviewees shared additional personal stories that provided useful background information for readers to understand their situation during the pandemic.
In addition to these personal narratives, “We and Equality” also published a 44-question “Women's Mental Health Questionnaire” on WeChat, asking about respondents’ experience during the pandemic, including their sense of belonging, care/housework commitments, sleep quality, emotional and mental status, feeling about quarantine, lockdown, illness or death of loved ones, and attitudes towards the government’s COVID-19 policies. The questionnaire received a total of 453 valid responses. Based on the responses, “We and Equality” has compiled a bilingual data analysis report.
”We and Equality" is a grass root project started in November 2016. Through the WeChat public account, they publish articles weekly to raise awareness and share knowledge on gender-related issues in China. They also organize in-person activities bi-weekly where people gather for in-depth discussion, and foster a community to promote gender equality.
Film and Video
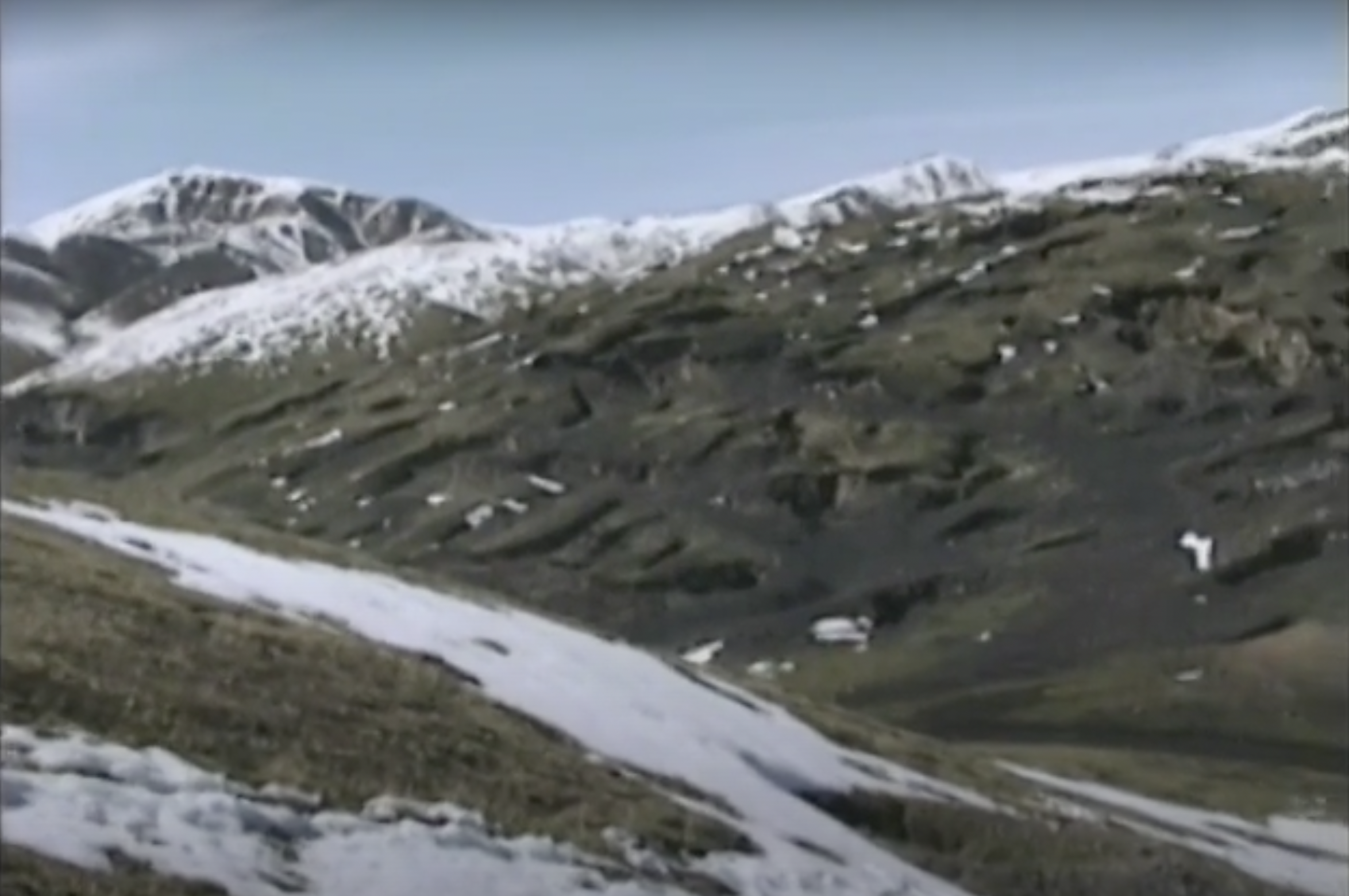
Faraway Mountain
This movie captures the lives of miners in small coal mines in the Qilian Mountain area of Qinghai Province. At 3600 meters above sea level, the air here is thin. Miners in the small coal kilns labor hard in a working environment without any protection, and usually get silicosis after 5-10 years of work, thus losing their ability to work. If they die in an accident, their families receive only meager compensation. This is a true record of the survival of China's grassroots laborers in the early 1990s.
Book
Killing and Hijacking: Tibet's Cultural Revolution Through the Lens
In 1966, when the flames of the Cultural Revolution began to spread, writer Tsering Woeser (唯色) was born in the General Hospital of the Tibetan Military Region. Her father was an officer in the People's Liberation Army (PLA) in Tibet at the time, and an avid photographer. Through his camera lens, the officer recorded the most comprehensive collection of images of the Cultural Revolution in Tibet to date. Tsering Woeser, on the other hand, restores and records the story behind the camera lens: It was an attempt to fight against oppression and preserve the true history of Tibet during the Cultural Revolution.
Book
Life of Storms: The New Life of a Disabled Prisoner, A
On August 8, 1966, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China adopted the "Sixteen Articles" of the Cultural Revolution. Soon after, Liu Wenhui, a young mechanic in Shanghai who had been labeled as a Rightist in 1957, wrote pamphlets and leaflets clearly opposing the Cultural Revolution, the "Sixteen Articles," authoritarianism, and tyranny. Liu was arrested on November 26 of that year. Four months later, he was executed for "counter-revolutionary crimes." Liu Wenhui became the first person known to have been publicly shot for opposing the Cultural Revolution. The author of this book, Liu Wenzhong, was Liu Wenhui's co-defendant and survived thirteen years in prison. In this autobiography, Liu Wenzhong describes in detail not only Liu Wenhui's ideology but also how he was killed by the tyrannical government.
Book
My Western Region, Your Eastern Land
The first edition of this book was published two years before the landmark event on July 5 in Urumqi from which the ethnic problems in Xinjiang erupted. The "July 5 Incident" was an ethnic vendetta in Urumqi that resulted in thousands of deaths and injuries. It has been regarded as a turning point in the all-out hostility between Uyghurs and Han Chinese and in the shift of Xinjiang's governance from economic development to political high-handedness. The book is thus considered prescient and ahead of its time. Before writing the book, Wang Lixiong had been imprisoned for more than 40 days on the charge of "stealing secret state documents." But this imprisonment brought him a great reward: he was to meet Muhtar, an ethnic Uyghur who was also a political prisoner. "It was because of Muhtar that the book took on a new perspective," says Wang Lixiong. Xinjiang is no longer a symbol in documents, books and materials, but has real flesh and blood, emotions, and even body heat.
Book
Sky Burial: The Fate of Tibet
In this book, author Wang Lixiong presents his arguments with a great deal of personal experience and field work. The book covers the history of the Tibetan issue, the current situation, and various aspects. The book was first published by Mirror Books in Hong Kong in 1998, and an updated edition was released in 2009.
Film and Video
Songs of Maidichong Village, The
This film was shot in a village called Maidichong in the mountains of Yunnan Province. The village is inhabited by a community of Miao people who are Christians. 100 years ago, the British missionary, Mr. Burghley, came to this village, fostered the Miao language, and brought faith, education, and medical care to the Miao people. This movie tells this history and how their journey of faith was brutally suppressed during the Cultural Revolution. It also presents the challenges they face today.
Book
Tibet in Agony: Lhasa 1959
Traveling Chinese history scholar Li Jianglin began working on the Tibet issue in 2004. She has traveled to India every year in search of Tibetan refugees, visited 14 Tibetan refugee settlements in India and Nepal, contacted more than 200 exiled Tibetans from the three regions of Tibet, and personally interviewed the Dalai Lama in Dharamsala, the seat of the Tibetan government-in-exile, in 2008. In 2010, Li Jianglin completed her book <i>Lhasa 1959!</i> by drawing on interviews, information searches, and rare historical photographs provided by the Tibetan government in exile, in the hope of reconstructing the little-known history of the Dalai Lama's departure from Tibet in 1959. The book was published by Taiwan's Lianjing Publishing House in 2010 and reprinted in 2016.
Book
When the Iron Bird Flies: China's Secret War in Tibet
Around the eighth century A.D., the founder of Tibetan Buddhism, Guru Rinpoche, prophesied, "When the iron bird flies in the sky and the iron horse runs on the earth, the Tibetans will be dispersed all over the world like ants, and the Buddha's Dharma will be spread into the land of the red people." More than 1,000 years later, in the middle of the 20th century, the Chinese Communist Party drove the "iron bird" across the sky and rode the "iron horse" across the plateau. The Tibetans courageously rose up to resist resulting in with countless deaths countless deaths. Those who survived were forced to leave their homeland and live in exile in India, drifting around the world. Thus, the prophecy came true. From a military point of view, the Tibetan war in Tibet was a victory, but it received only minimal publicity. The official version of the Party's history is either vague or evasive about the bloody massacre during the entry into Tibet, attempting to cover it up by "suppressing armed rebellion" and "purging counter-revolutionaries". More than sixty years later, this war has yet to be demystified. Li Jianglin, an independent scholar, was moved by the tragedy of the war and the plight of the Tibetans, and endeavored to restore the historical facts. Since 2004, she has devoted herself to research, visiting hundreds of Tibetan elders, searching for tens of thousands of historical materials, collecting military archives, and comparing them with the official published materials of the Communist Party of China, in order to present memories of past, little by little.
Book
Who is the New China
Author Xin Hao Nian tries to analyze the modern history of China since the Xinhai Revolution. He pointsout that the People's Republic of China (PRC) is a restoration of the authoritarian system, and the Republic of China (ROC) represents China's road to a republic. The first volume of the book defends and clarifies the history of the Kuomintang (KMT), arguing that the KMT is not a "reactionary faction" as claimed by the CCP. The second volume criticizes the revolution and history of the CCP. The book was first printed in 1999 by Blue Sky Publishing House (USA) and reprinted in June 2012 by Hong Kong's Schaefer International Publishing. It is banned on the mainland.
Book
Zhu Xueqin Anthology
A collection of essays by Zhu Xueqin, a Chinese liberal intellectual. He has faced and criticizes various problems in China from a liberal point of view. Most of Zhu Xueqin's books were later banned.
Book
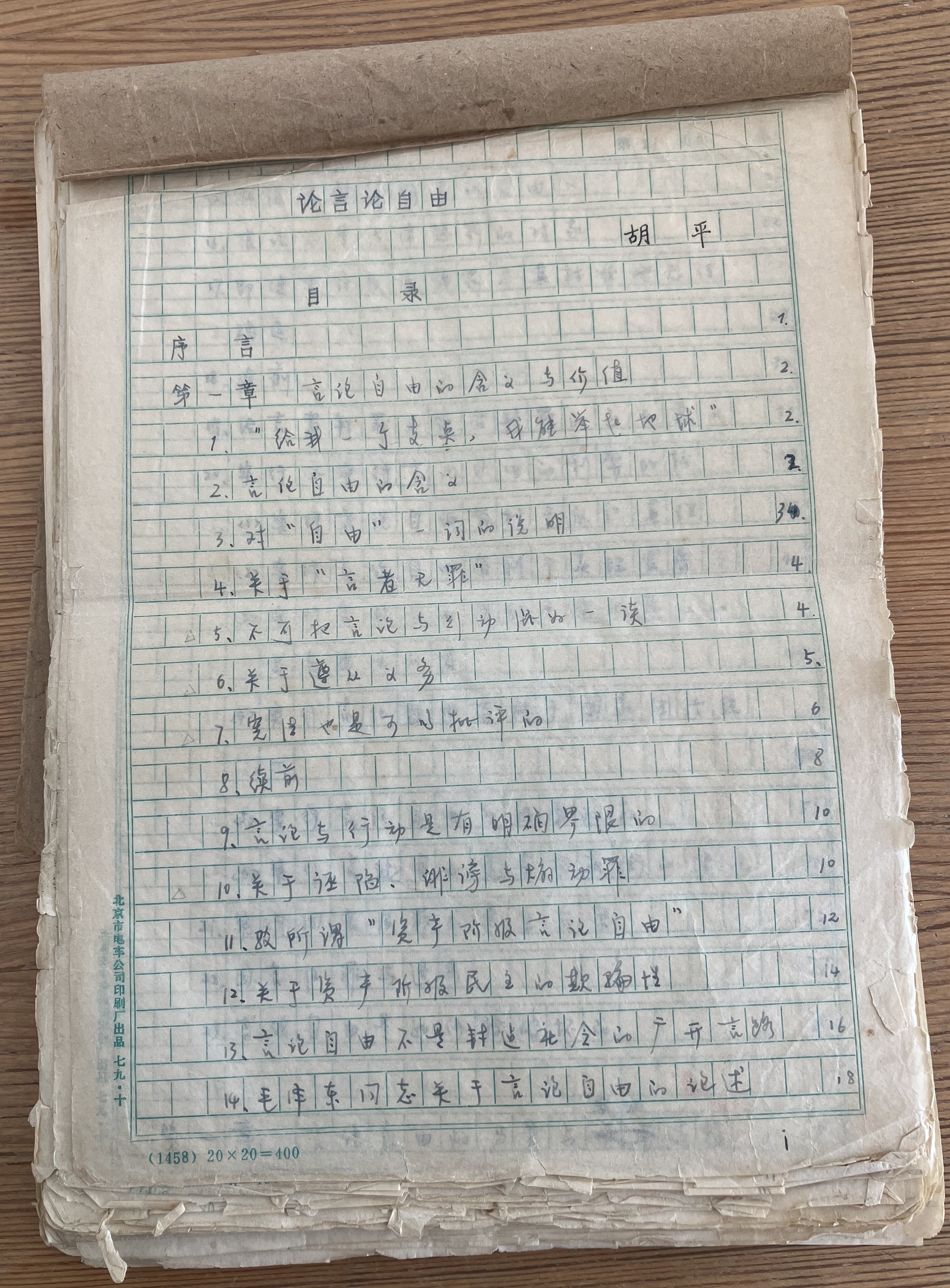
On Freedom of Speech
“On Freedom of Speech” is a treatise by Hu Ping. It was first published in 1979. A revised version was published in 1980, when Hu ran for local elections at Peking University. The treatise was later published in Hong Kong in 1981 and again in a Chinese journal in 1986. Multiple publishing houses in China made plans to distribute the treatise in book form, but China’s anti-liberalization campaign prevented the books from publishing.
“On Freedom of Speech” explains the significance of freedom of speech, refutes misunderstandings and misinterpretations of freedom of speech, and proposes ways to achieve freedom of speech in China.
This document, provided by the author, also includes the content of the symposium held after the publication of “On Freedom of Speech” in 1986, as well as the preface written by the author in 2009 for the Japanese translation of this treatise.